EmoUS: Simulating User Emotions in Task-Oriented Dialogues 논문 읽기
EmoUS: Simulating User Emotions in Task-Oriented Dialogues
Abstract
기존의 task-oriented 대화 시스템을 위한 사용자 시뮬레이터(US)는 사용자 페르소나(persona)와 감정을 고려하지 않고, 의미적 및 자연어 수준에서만 사용자 행동을 모델링합니다. 다양한 감정 상태에 의해 유발되는 다양한 사용자 행동을 모델링하지 못하는 일반적인 사용자 정책으로 대화 시스템을 최적화하는 것은, 실제 환경에서 높은 이탈률(drop-off rate)을 초래할 수 있습니다. 따라서 우리는 사용자 행동과 함께 감정을 시뮬레이션할 수 있는 사용자 시뮬레이터인 EmoUS를 제안합니다. EmoUS는 사용자 목표, 대화 이력, 사용자 페르소나에 기반하여 사용자 감정, 의미적 행동, 자연어 응답을 생성합니다. 시스템의 특정 행동이 어떤 사용자 감정을 유발하는지 분석함으로써, EmoUS는 다양한 대화 시스템을 평가하고 특히 사용자의 감정 상태에 미치는 영향을 평가하는 도구로 사용할 수 있음을 보여줍니다. 이러한 방법을 개발하는 것은 대형 언어 모델 기반 챗봇이 증가하고 윤리적 문제가 대두되는 시대에 중요합니다.
Introduction
ToD 시스템은 강화학습을 사용해 학습하는 경우가 있는데, 이 방법은 시스템과 사용자의 상호작용을 요구한다. 이 과정에서 실제 사용자 (사람)과 함께 훈련하는 것은 많은 비용과 시간을 필요로 하기 때문에 User simulator를 구축하는 것은 대안이 될 수 있다.
최근 User simulator의 연구에서는 자연어 또는 행동을 통해 사용자의 외재적 상태를 구현했지만, 사용자의 감정 상태나 persona 같은 내재적 상태를 구현하는 것이 빠져있다. 일반적인 사용자에 대한 설정은 언어적 다양성이 제한될 수 있으며, 다양한 사용자의 감정에 의해 유발되는 다양한 행동을 표현하지 못한다.
본 논문에서는 대화 기록과 사용자의 Persona에 따라 감정 상태를 modeling하는 User simulator를 제안한다.
- 사용자 감정, 의미적 행동, 그리고 자연어 발화를 포함하는 user simulator EmoUS를 제안
- EmoUS는 사용자 정책과 감정을 함께 모델링하여 동일한 상황에서도 언어적 다양성이 증가한다.
- EmoUS의 사용자 감정은 단순한 과제 성공률 이상의 미묘하고 세부적인 평가를 제공하여 대화 시스템(DS)을 평가하는 데 중요한 통찰을 제공한다.
SIMULATING USER EMOTION IN TASK-ORIENTED DIALOGUES
ToD task는 domain intent slot slot-value로 이뤄진 ontology에 의해 뒷받침된다.
ToD에서 사용자는 아래처럼 정의된 Goal을 가진다고 가정할 수 있다.
\[G = \{d_1:[(s_1, v_1), ...], d_2:[(s_3,v_3), ...], ...\}\]Semantic user actions와 system actions는 (𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑡, 𝑑𝑜𝑚𝑎𝑖𝑛, 𝑠𝑙𝑜𝑡, 𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒)로 구성된 튜플로 이뤄져있다. Semantic user actions는 자연어 발화로 변환될 수 있다.
대화에서 사용자의 감정은 다양한 요인에 의해 촉발되거나, persona와 관련이 있다. 예를 들어 시스템이 적절한 응답을 하지 않으면 사용자는 불만을 느낄 수 있고, persona는 이런 이벤트 등으로 도출되는 사용자의 감정을 나타낼 수 있다.
박물관 방문에 대해 흥분한 공손한 사용자 persona는 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑠𝑜𝑛𝑎 = {user: polite, attraction: excited}로 표현될 수 있다. User persona는 학습 중 대화 기록에서 도출될 수 있으며, 추론을 위해 샘플링될 수 있다.
감정을 포함한 사용자 시뮬레이션은 Seq2Seq 문제로 볼 수 있다. 각 턴마다 EmoUS는 대화 기록, 사용자 목표, 사용자 persona와 같은 context를 기반으로 사용자의 감정을 예측하고, semantic actions와 자연어 응답을 생성한다.
Model structure
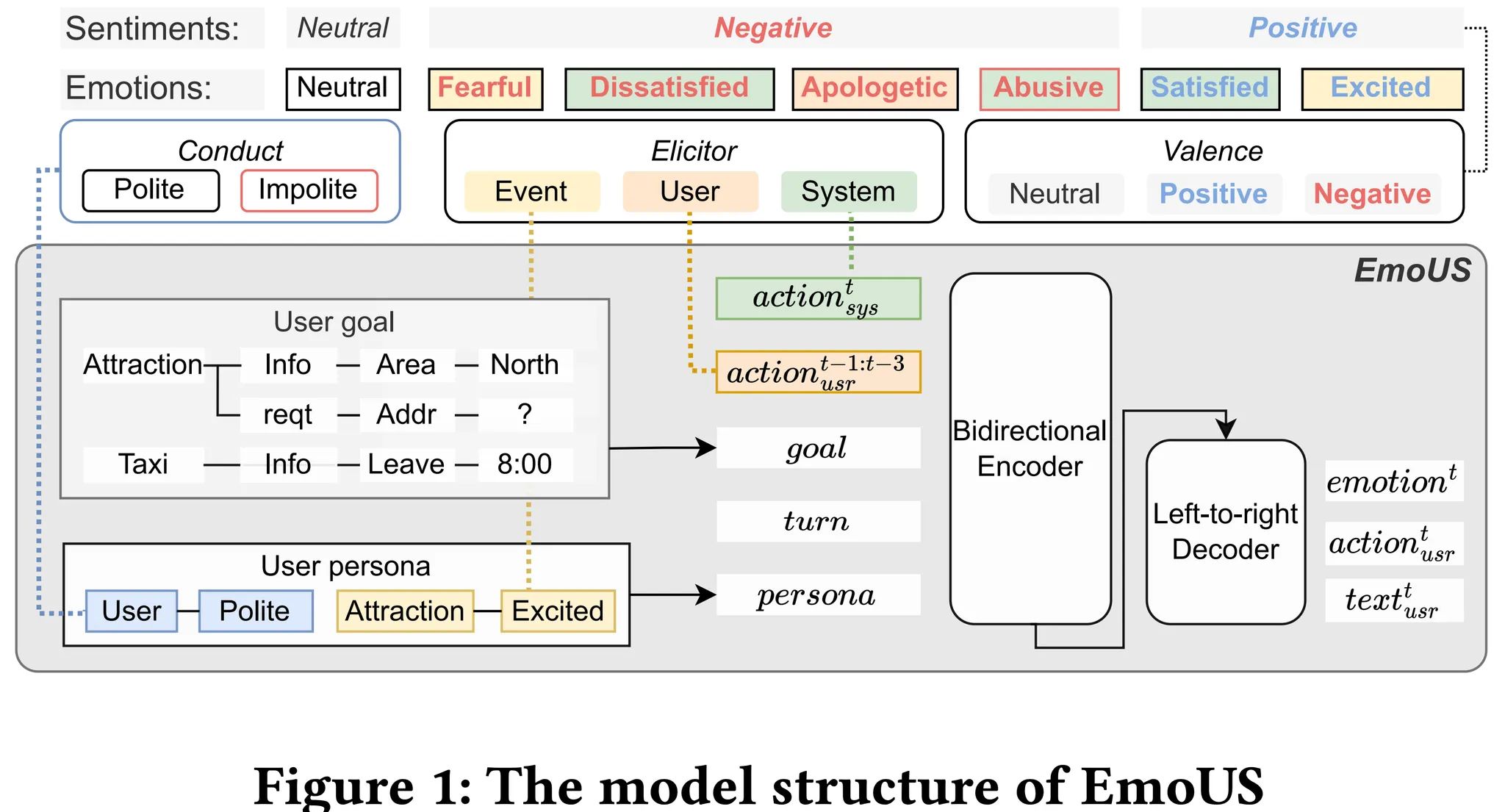
EmoUS는 turn t마다 입력으로 system action, user action history, user goal, turn information, user persona를 받고, user emotion, semantic action, utterance를 출력으로 생성한다.
Input
\[(action_{sys}^{t}, action_{user}^{t-1:t-3}, goal, turn, persona)\]Output
\[(emotion, action_{user}^t, utterance_{user}^t)\]semantic action (system, user action)
시스템과 사용자의 행동을 표현 (domain, intent, slot, value)
User: "I'm looking for a swimming pool in town."
System: "There are four swimming pools in Cambridge. Did you want one in a particular part of town?"
System action: {
"Attraction-Request": [
[
"Area",
"?"
]
],
"Attraction-Inform": [
[
"Area",
"Cambridge"
],
[
"Type",
"swimming pools"
],
[
"Choice",
"four "
]
]
}
User: "No, actually it doesn't matter. Can you suggest one and provide me the postcode?"
User action: {
"Attraction-Request": [
[
"Post",
"?"
]
]
}
User Goal
"goal": {
"taxi": {},
"police": {},
"hospital": {},
"hotel": {},
"attraction": {
"info": {
"type": "swimmingpool"
},
"reqt": [
"postcode"
],
"fail_info": {}
}
}
Turn information
t 번째 turn임을 표시
Persona
자세하게 설명되어 있지는 않음, 아마 emotion token을 사용하는 것으로 생각됨
𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑠𝑜𝑛𝑎 = {user: polite, attraction: excited}
앞서 설명했듯이 동일한 context를 사용하더라도 user persona와 감정에 따라 다양한 출력이 발생한다.
EmoUS는 EmoWOZ 데이터셋에서 제공하는 elicitor, conduct, valence를 사용했다.
Elicitor: 감정이 추출되는 곳으로 user, event, system이 있고, 여기서는 persona, system action, user action이 될 수 있다.
Conduct: 사용자가 정중한지 아닌지 - persona로 설정한다.
Valence: 감정극성(?) 좋은지 싫은지
EmoUS는 json formatted word seqeunce를 생성하는 seq2seq 모델이다. BART를 Finetuning해서 사용한다.
입력:
{
"system": action,
"user": action_user,
"goal": goal,
"turn": t,
"persona": persona
}
출력:
{
"action": action,
"emotion": emotion and sentiment,
"text": text
}
EmoWOZ
emotion label
| Label | Emotion Tokens | Valence (sentiment) | Elicitor | Conduct |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Neutral | Neutral | Any | Polite |
| 1 | Fearful, sad, … | Negative | Event / fact | Polite |
| 2 | Dissatisfied, dislike, … | Negative | Operator | Polite |
| 3 | Apologetic | Negative | User | Polite |
| 4 | Abusive | Negative | Operator | Impolite |
| 5 | Excited, happy, … | Positive | Event / fact | Polite |
| 6 | Satisfied, liking | Positive | Operator | Polite |
Data example
Goal에 대한 정보가 주어지고, 검색 대상에 대한 값과 얻어야하는 정보가 주어짐
이것들을 줄글로도 설명함
-
Goal example
"goal": { "taxi": {}, "police": {}, "hospital": {}, "hotel": {}, "attraction": { "info": { "name": "cineworld cinema" }, "reqt": [ "area" ], "fail_info": {} }, "train": { "info": { "destination": "cambridge", "day": "monday", "arriveBy": "18:00", "departure": "norwich" }, "reqt": [ "duration", "price", "leaveAt" ], "fail_info": {} }, "message": [ "You are looking for information in Cambridge", "You are looking for a <span class='emphasis'>train</span>. The train should depart from <span class='emphasis'>norwich</span> and should go to <span class='emphasis'>cambridge</span>", "The train should <span class='emphasis'>arrive by 18:00</span> and should leave on <span class='emphasis'>monday</span>", "Make sure you get <span class='emphasis'>travel time</span>, <span class='emphasis'>price</span>, and <span class='emphasis'>departure time</span>", "You are also looking for a <span class='emphasis'>particular attraction</span>. Its name is called <span class='emphasis'>cineworld cinema</span>", "Make sure you get <span class='emphasis'>area</span>" ], "restaurant": {} }
이런식으로 대화 기록과 발화마다의 정보 값들이 주어짐
-
Log example
"log": [ { "text": "I'm looking for a swimming pool in town.", "emotion": [ { "emotion": 0, "sentiment": 0 } ], "dialog_act": {}, "span_info": [] }, { "text": "There are four swimming pools in Cambridge. Did you want one in a particular part of town?", "emotion": [], "dialog_act": { "Attraction-Request": [ [ "Area", "?" ] ], "Attraction-Inform": [ [ "Area", "Cambridge" ], [ "Type", "swimming pools" ], [ "Choice", "four" ] ] }, "span_info": [ [ "Attraction-Inform", "Area", "Cambridge", 6, 6 ], [ "Attraction-Inform", "Type", "swimming pools", 3, 4 ], [ "Attraction-Inform", "Choice", "four", 2, 2 ] ] }, { "text": "No, actually it doesn't matter. Can you suggest one and provide me the postcode?", "emotion": [ { "emotion": 0, "sentiment": 0 } ], "dialog_act": { "Attraction-Request": [ [ "Post", "?" ] ] }, "span_info": [] }, { "text": "Yes, the Jesus green outdoor pool get the most consistently positive feedback, their postal code is cb43px, can I help with anything else?", "emotion": [], "dialog_act": { "Attraction-Recommend": [ [ "Post", "cb43px" ], [ "Name", "Jesus green outdoor pool" ] ], "general-reqmore": [ [ "none", "none" ] ] }, "span_info": [ [ "Attraction-Recommend", "Post", "cb43px", 18, 18 ], [ "Attraction-Recommend", "Name", "Jesus green outdoor pool", 3, 6 ] ] } }
다양한 emotion, sentiment 예시
{
"text": "Hello, are you still there? You said that you would reserve it but never did anything, it has been 55 minutes.",
"emotion": [
{
"emotion": 2,
"sentiment": 1 (Negative)
}
]
"text": "No, thank you. That was all I needed. Thanks. Bye. ",
"emotion": [
{
"emotion": 6,
"sentiment": 2 (Positive)
}
],
}
EXPERIMENTAL SETUP
EmoUS가 사용자의 감정을 예측하는 것이 ToD 시스템을 평가하는데 의미있는 역할을 하는 것을 보인다.
Supervised learning for emotion simulation
sentiments, emotion의 macro-F1 score를 측정하여 성능을 평가한다.
비교 모델은 대화 이력을 바탕으로 sentiment, user action, utterances를 생성하는 SatActUtt 모델이다.
Interacting with DS
특정한 사용자 시뮬레이터(US)로 학습된 대화 시스템(DS)을 다른 US로 평가하는 교차 모델 평가 방식을 통해 US의 성능을 평가한다.
DS에는 사용자의 발화를 이해하기 위해 BERT로 구성된 NLU 모듈과 ConvLab-3 framework에서 사용자의 상태를 추적하기 위한 규칙 기반 dialogue state tracking 모듈도 포함된다.
논문에서는 다양한 시스템 행동이 사용자 감정을 어떻게 유발하는지 분석하기 위해 EmoUS와 EmoUS로 학습된 DS 사이의 1000개의 대화를 사용했다.
시스템의 행동을 아래와 같이 구분했다.
confirm - 시스템이 사용자가 제공한 슬롯과 값을 반복함
no_confirm - 시스템이 해당 정보를 반복하지 않음
miss_info - 시스템이 사용자가 방금 언급한 정보를 요청함
neglect - 시스템이 사용자의 요청에 응답하지 않음
reply - 시스템이 사용자의 요청에 응답함
loop - 시스템이 두 턴 연속으로 동일한 행동을 수행함.
EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
User emotion modelling
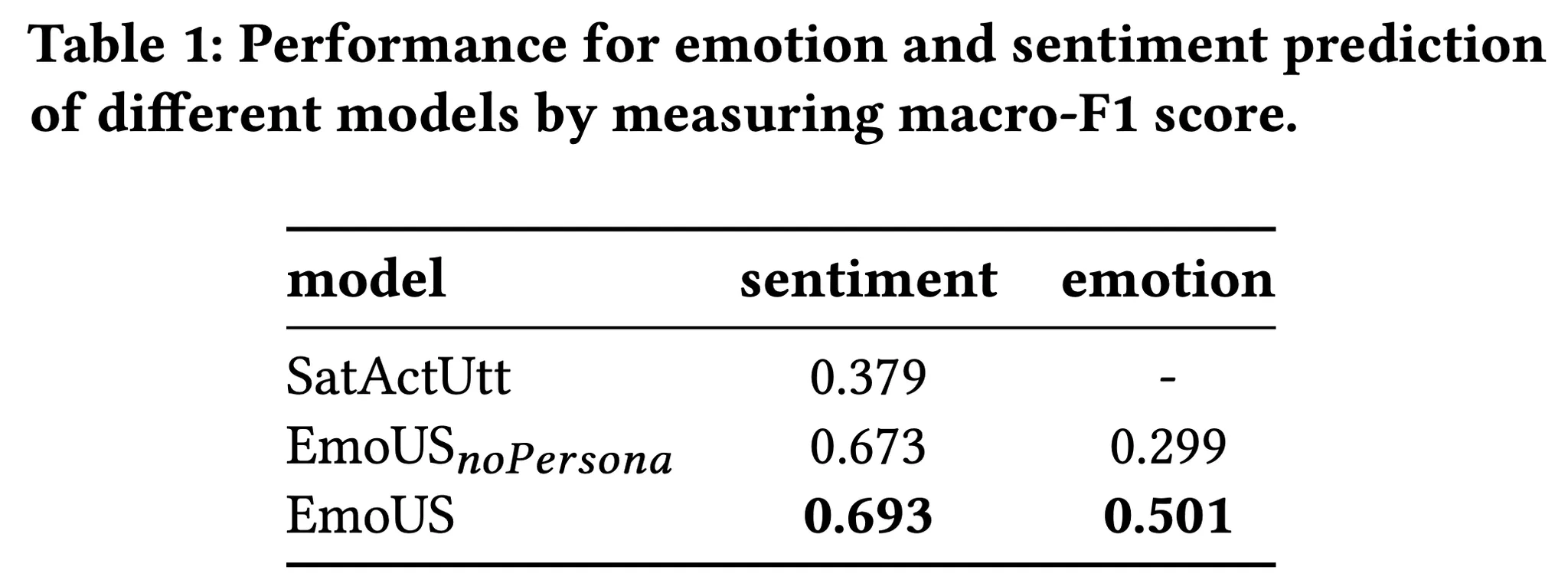
sentiment classification에서 본 논문에서 제안한 모델인 EmoUS가 비교 모델 SatActUtt보다 더 좋은 성능을 보인다.
또한 Persona를 사용하지 않은 모델(noPersona)보다 사용한 모델이 emotion을 예측하는데 더 좋은 능력을 보인다. 이는 persona를 고려하는 것이 emotion을 예측하는데 도움이 된다는 것을 보여준다.
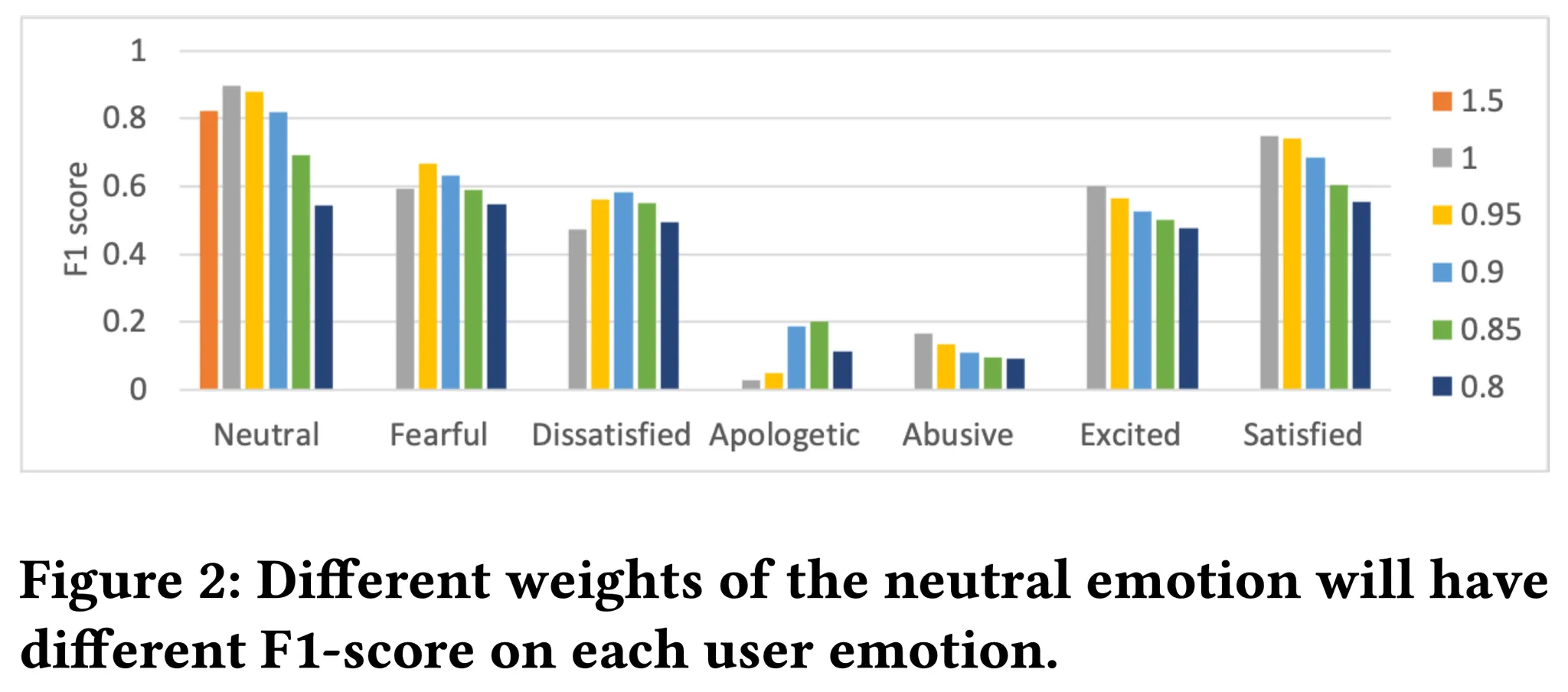
Neutral 감정의 확률에 가중치 𝑤를 주어 simulation을 다양하게 만들 수 있다. 가중치가 높을수록 Neutral 감정이 선택될 가능성이 증가한다. 그림 2에서 𝑤 = 1.5일 때 EmoUS는 Neutral만 선택하게 된다. 가중치가 줄어들수록 다양한 감정을 나타낸다.
𝑤 = 0.95일 때 두려움에 대해 최고의 성능을 나타내고, 𝑤 = 0.9일 때 불만족, 𝑤 = 0.85일 때 사과에 대해 최고의 성능을 보였다. 따라서 가중치를 조정하여 다양한 사용자 행동을 유도할 수 있습니다.
User action prediction
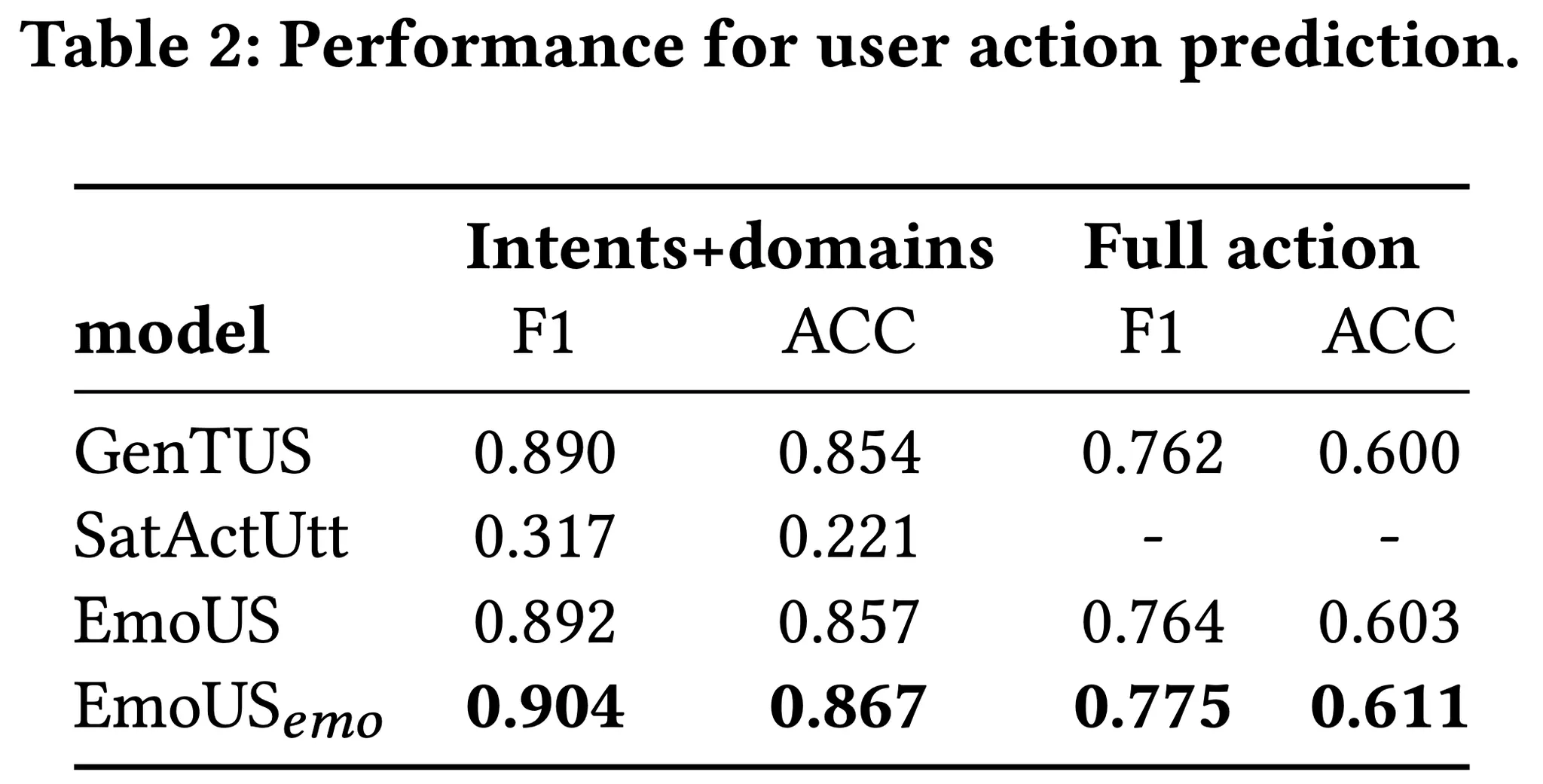
모델의 semantic action 생성 능력을 평가한다.
EmoUS_emo는 Gold emotion을 바탕으로 semantic action을 생성한다.
EmoUS는 goal을 고려하여 semantic action을 생성하기 때문에 이를 고려하지 않는 SatActUtt보다 좋은 성능을 보인다.
또한 emtion과 sentiment를 동시에 생성하는 더 복잡한 task를 가짐에도 불구하고 semantic action만 생성하는 GenTUS보다 좋은 성능을 보인다.
Natural language evaluation
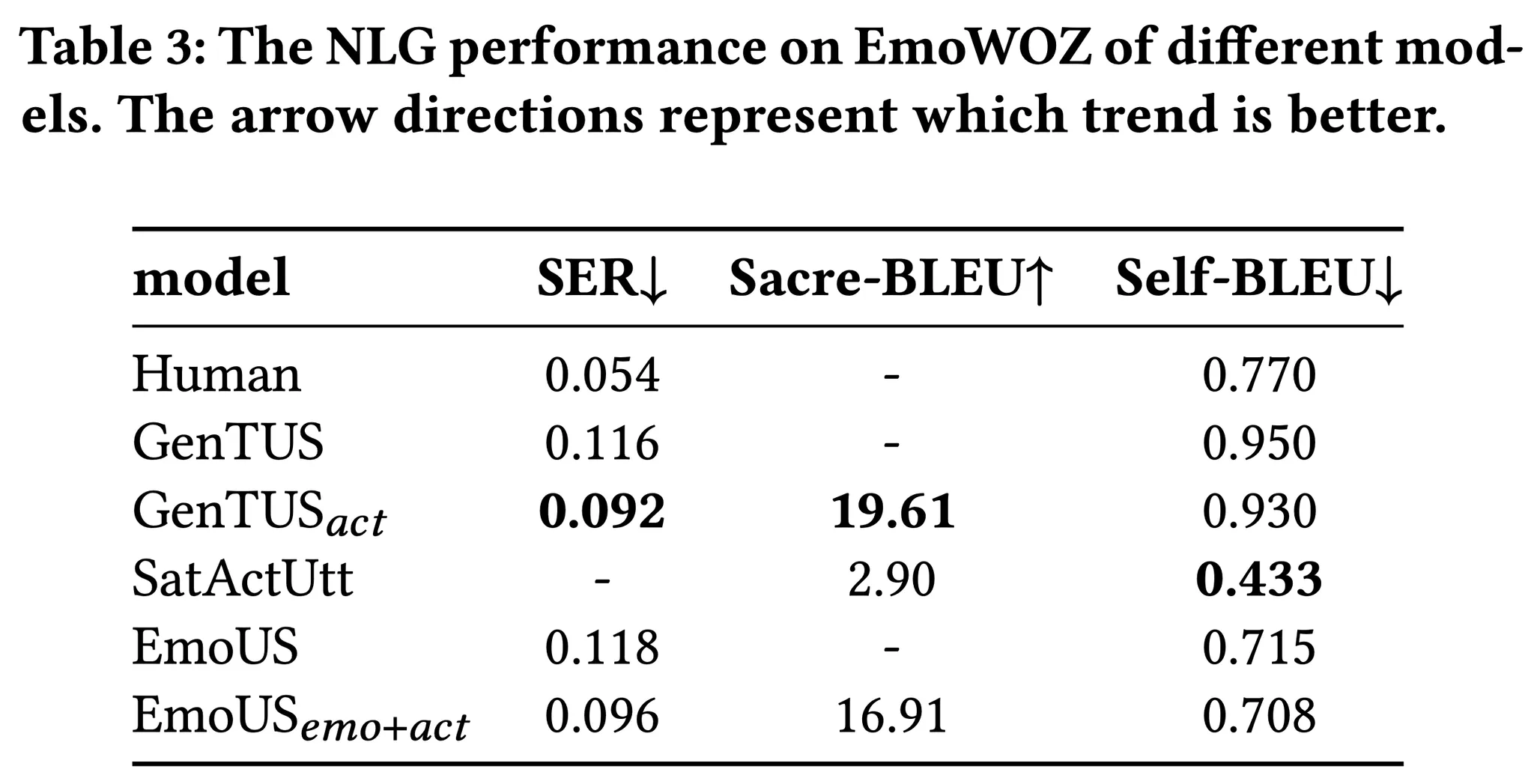
여기서는 모델의 자연어 생성 능력을 평가한다.
SatActUtt는 낮은 Self-BLEU를 기록해 다양한 발화를 하는 것으로 볼 수 있지만 Gold utterance와 비교하는 Sacre-BLEU 점수가 낮아 user goal과는 관련 없는 다양한 발화를 하는 것으로 해석할 수 있다.
반면 EmoUS는 GenTUS와 다른 성능은 비슷하지만 더 낮은 Self-BLEU를 기록해 감정에 따른 더 다양한 발화를 생성하는 것으로 보인다.
Cross-model evaluation
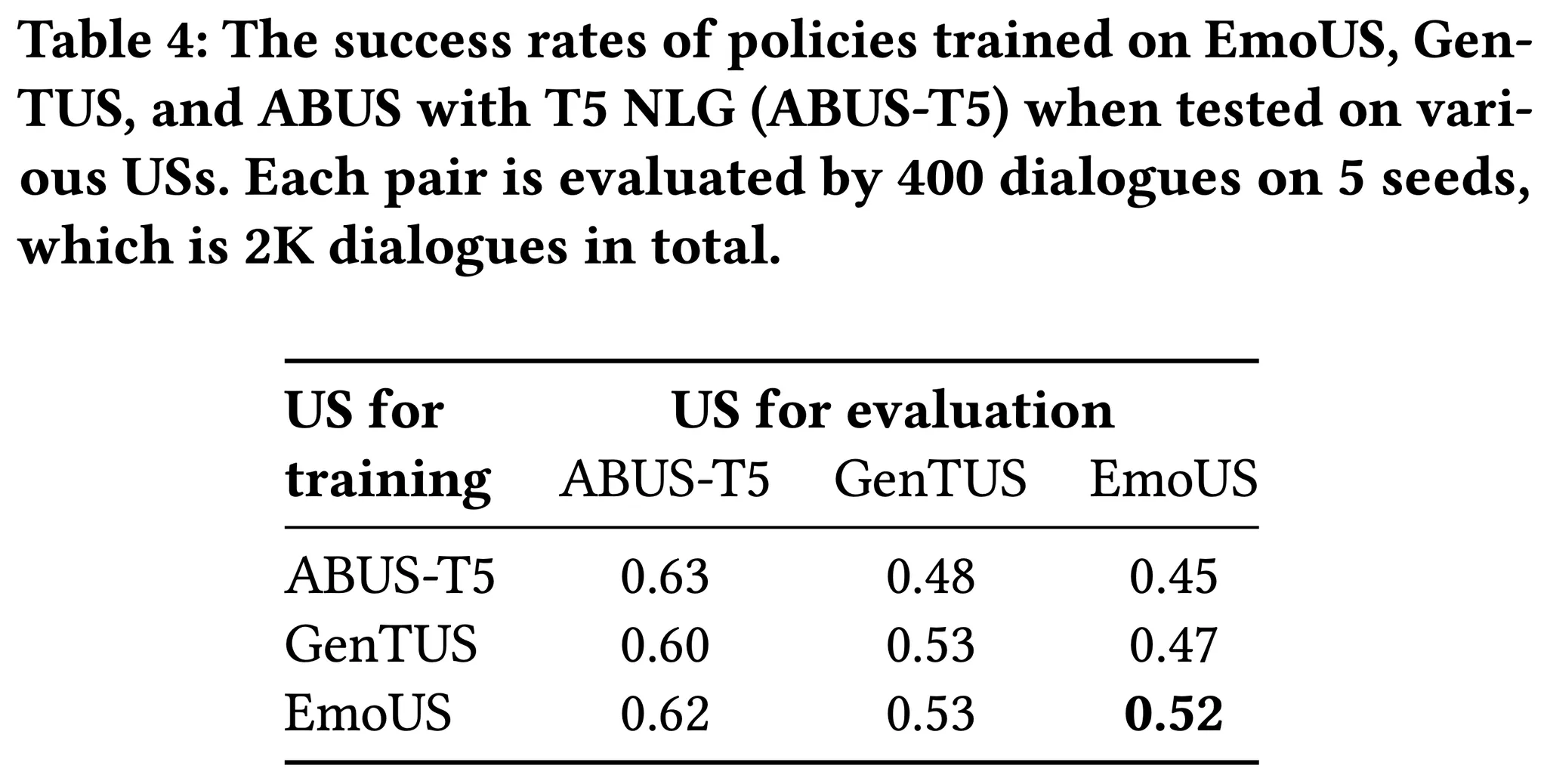
EmoUS로 학습한 Dialogue System이 다른 것으로 학습한 DS에 비해 전반적으로 높은 성공률을 보인다.
따라서 EmoUS가 DS를 학습할 때 더 좋은 학습 환경을 제공한다.
System behaviour with the user emotions
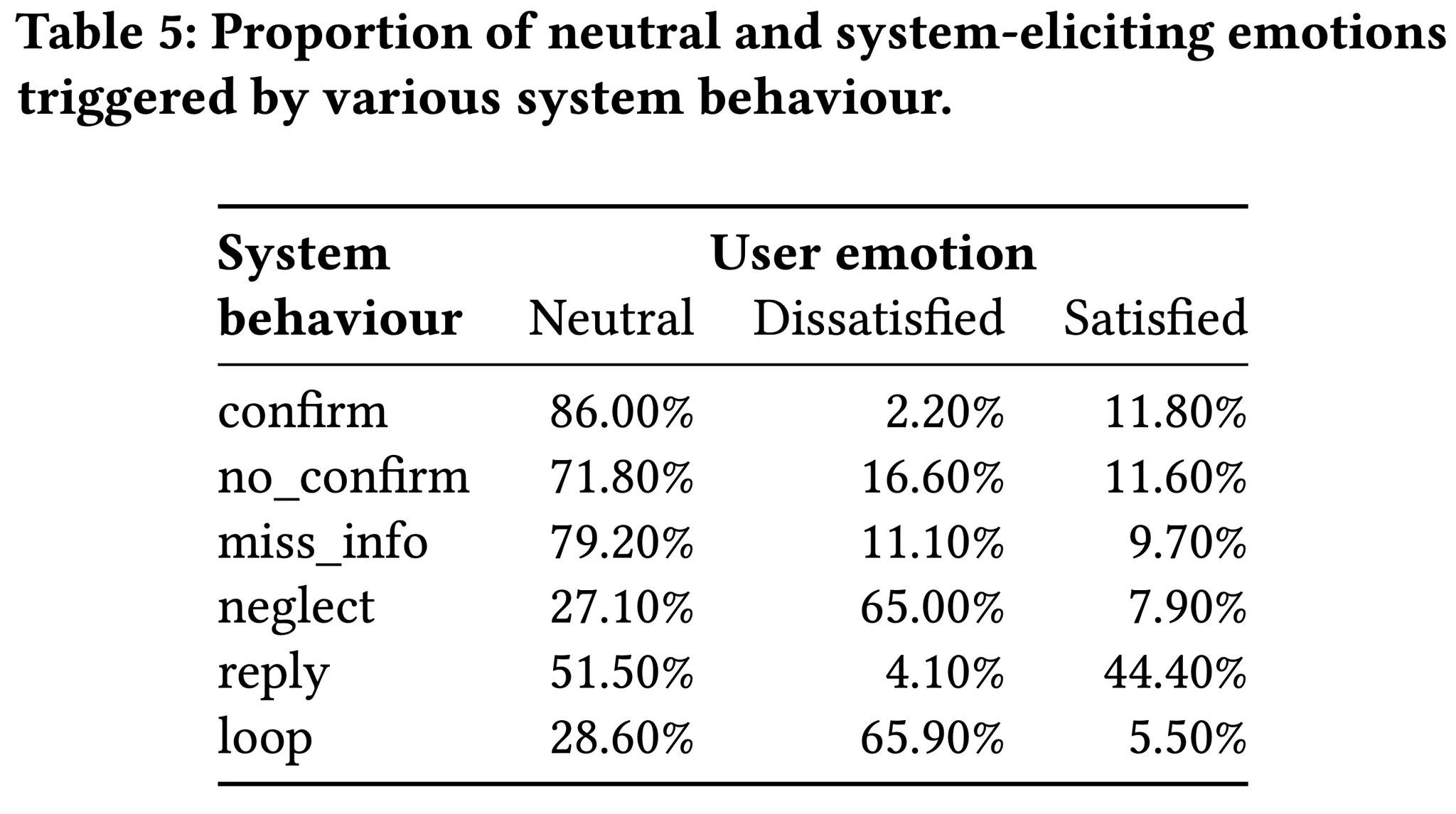
EmoUS와 이걸 사용해 학습한 DS 사이의 대화 1k개를 분석했을때,
system이 제대로 답변을 못하면 (neglect, loop) 사용자의 불만족도가 올라간다.
반대로 잘 답변하면 (reply) 만족도가 올라간다.
이는 이전연구 (Simulating user satisfaction for the evaluation of task-oriented dialogue systems)에서 주장하는 내용과 비슷하다.
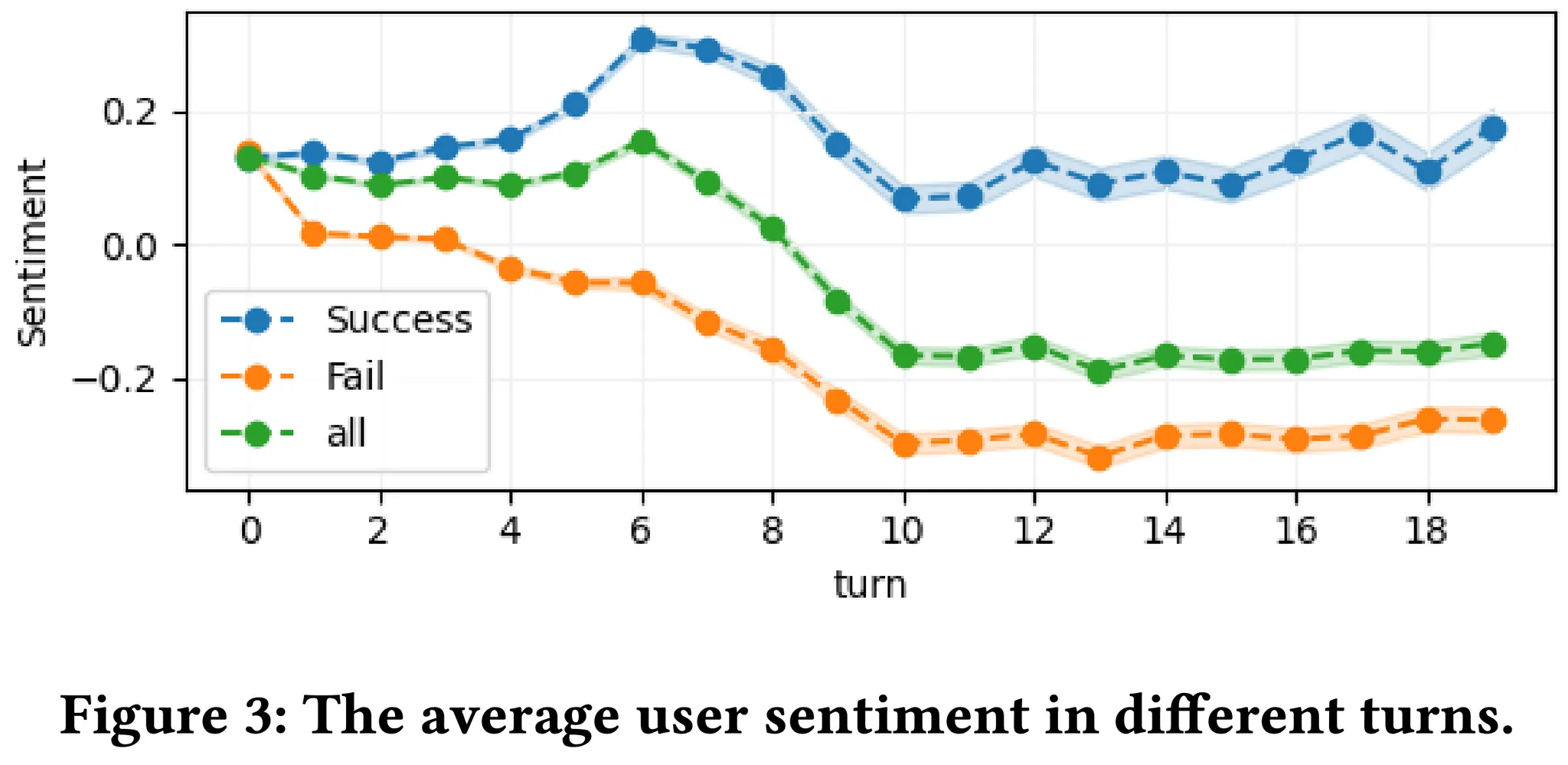
사용자의 각 턴마다 감정을 숫자로 평균냈을 때, 변화이다. (긍정 +1, 보통 0, 부정 -1)
전반적으로 성공적인 대화일 때 긍정적인 점수가 높고, 실패한 대화일 때 부정적이게 된다.
6번째 turn 이후에는 급격히 부정적이게 되는데 이는 사용자가 그 이후부터 인내심이 떨어지는 것으로 생각된다.
Conclusion
본 논문에서는 감정 상태를 생성하고 이를 바탕으로 더 다양한 발화를 생성하는 EmoUS를 제안한다.
논문의 실험 결과는 대화 시스템이 사용자 감정 상태에 미치는 영향을 조사하는 데 EmoUS가 유용하다는 것을 보여준다.
후속 연구로는 persona와 감정 간의 상관관계를 조사할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 시스템 응답이 부적절하더라도 예의 바른 사용자가 더 높은 만족도를 보이는지에 대한 연구가 있을 수 있다.
또한 시뮬레이션의 타당성을 확인하기 위해 human evaluation도 수행되어야 한다.

댓글남기기